Imagerie par résonance magnétique (IRM)
Diagnostics without radiation
Magnetic resonance tomography (MRT or nuclear spin tomography) does not use X-rays; instead, it uses a strong magnetic field and radio waves. The core of magnetic resonance tomograph is an electromagnet that weighs a ton, with a tube-shaped opening into which the patient pallet travels. In a short time, layered images are produced of every region of the body. A computer uses the digital data to calculate views of the region of the body being examined, which the radiologist then diagnoses.
Important areas of application for magnetic resonance tomography
Soft tissues such as the brain and spinal cord, internal organs (except for the lungs), as well as muscles and joints can be seen particularly well with MRT. Other important areas of application for magnetic resonance tomography is the precise representation of blood vessels, early detection of tumors, and insights into the metabolism. Mammography MRT and multiparametric imaging of the prostate have become important new examination fields. Virtual image analysis methods make the body’s internal processes visible to referring colleagues and to the patient.
Even organs that move, such as the beating heart, can now be banished from images. In the field of cardio MRT, the Radiology Baden-Baden practice has many years of expertise. Click here to learn more about cardiac diagnostics at Baden-Baden …
Advantages of magnetic resonance tomography
Magnetic resonance tomography is a gentle, practically risk-free examination method. Due to the lack of radiation load, even children and pregnant women can be examined. And if a patient is not able to tolerate contrast agents containing iodine, such as is used in computed tomography, the radiologist can often switch to magnetic resonance imaging for examination.
Our equipment
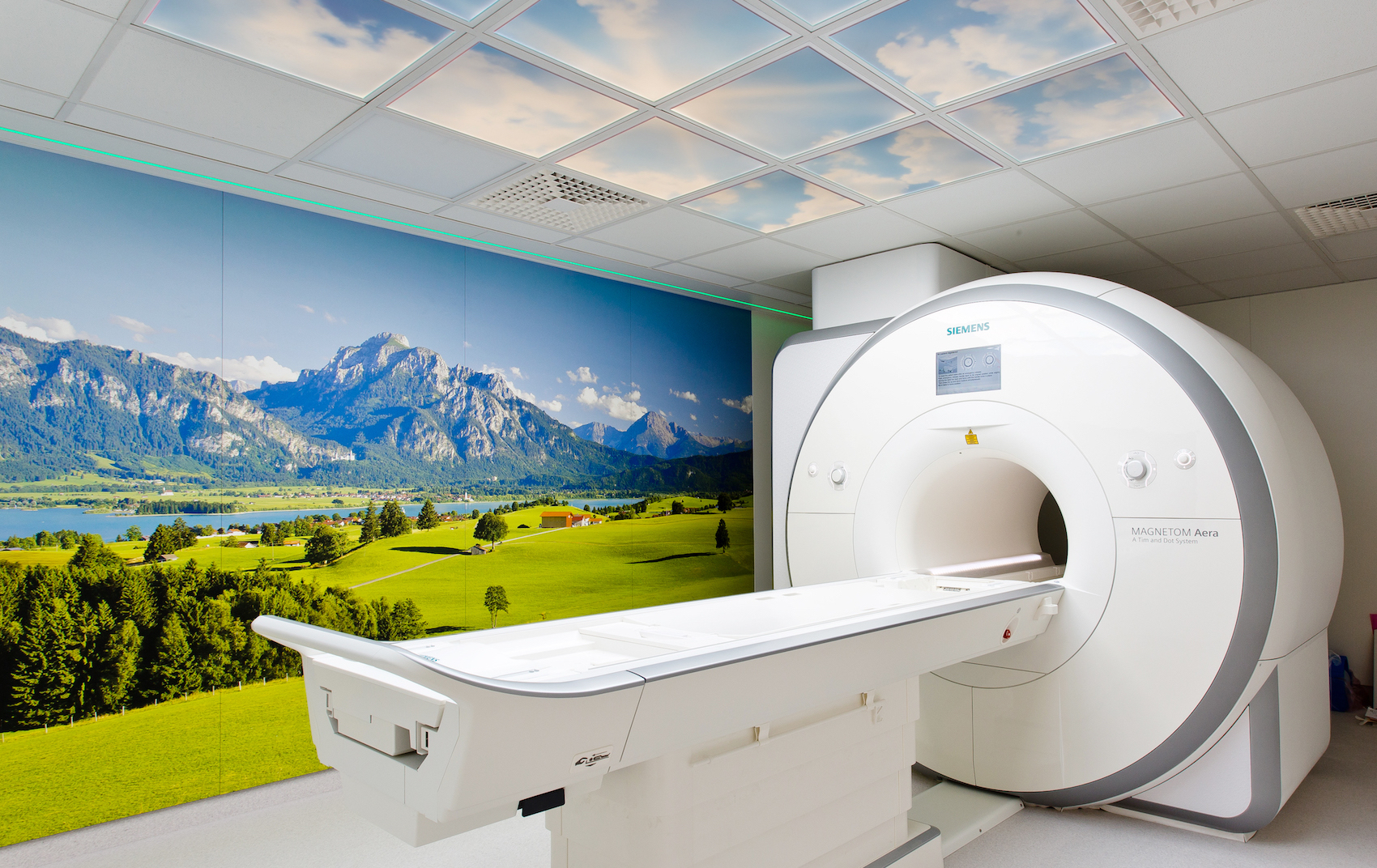
Our modern equipment includes a “semi-open” Siemens Aera MRT (1.5T) and two Symphonie TIM (1.5T) machine. Using cutting-edge, bright illumination technologies and sky simulations in the MRI examination room, our practice guarantees maximum patient comfort even during the examination. Click here to learn more about the MRT machines …
Typical application of MRT examination
Sports medicine and musculoskeletal MRI diagnostics
Typical indications
- High-resolution imaging of joints, tendons, ligaments, and muscle structures
- High-resolution representation of the spinal column
The Radiology Baden-Baden practice is an accredited specialist center for musculoskeletal imaging of the German X-ray Association (Deutschen Röntgengesellschaft). Click here to learn more about certificates held by Radiology Baden-Baden … One focal point of the practice is thus musculoskeletal imaging for diagnosing acute and chronic illnesses and injuries of the entire locomotor system in adults and children. Cartilage is of central importance to joint integrity. Unmatched representation of even early stages of cartilage loss using ultrahigh-resolution MRT. Injuries to ligaments, tendons, and intervertebral discs, as well as early forms of bone injuries and blood supply problems, can be depicted optimally. An exact diagnosis is the basis for early and efficient therapy. One particular area of expertise in the practice is the area of rheumatological imaging, so the practice serves one of the largest rheumatological clinics in Germany (ACURA-Klinik Baden-Baden).
The process does not use any X-ray radiation at all..
Skull MRI
Typical indications
- Stroke diagnosis, vascular diagnosis
- Tumor diagnostics
- Inflammation diagnostics (e.g., multiple sclerosis)
Magnetic resonance tomography (MRT) of the skull is a radiological examination method for precisely representing the brain and its adjoining structures.
The process does not use any X-ray radiation.
Abdomen / liver MRI
Typical indications
- Unclear abdominal pain, ruling out tumor
- Space-occupying mass in the liver
- Space-occupying mass in the abdomen
- Imaging of bile tracts without contrast agent (MRCP—magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography)
- Imaging of urinary tracts
Magnetic resonance tomography (MRT) of the abdomen or liver is a radiological examination method for imaging the structures in the abdominal and liver region using a magnetic field.
The process does not use any X-ray radiation.
Cardiology MRT
Typical indications
- Coronary heart disease (CHD), angina pectoris pain
- Status post heart attack, determining infarct size
- Heart function and heart pumping function after disease
- Heart muscle diseases and inflammation
- Congenital heart defects in childhood and adulthood
- Acquired valve defects
- Blood clots (thrombosis) or tumors in the heart.
The cardio MRT exam is performed in close cooperation with our registered colleagues, particularly cardiologists, and can supplement their exams. Due to rapid technological and scientific advancement, cardio MRT is currently an established method for clarifying various heart diseases and the risk of a heart attack. Cardio MRT is generally recognized as the most accurate method for measuring heart size and function, particularly for CHD. It is also the most accurate method for determining the size of a past cardiac infarction. Using a medication, the blood supply and pumping function under load can be reliably depicted, so that statements can be made not only about an infarction that has occurred, but also about areas of the heart that are at risk and need therapy. The process does not use any X-ray radiation at all. Please note the sometimes specific contraindications, particularly for cardiac imaging. Click here to learn more about contraindications for MRT, especially cardio MRT … Please always clarify in advance whether your insurer will cover at least part of the cost of the examination.
Preparation: avoid caffeinated beverages on the day of the examination, and do not take any erectile dysfunction medications (e.g., Viagra) for 24 hours prior to the examination.
The Radiology Baden-Baden practice has many years of expertise in the field of cardio MRT and works together closely with regional cardiologists and heart centers.. Click here to learn more about certificates held by Radiology Baden-Baden … A cardiologist is directly on hand for the exam, in addition to the radiologist, so that the exam can be individually optimized for the patient.
Click here to learn more about cardiac diagnostics at Baden-Baden …
Prostate MRI
Typical indications
- Suspicion of prostate carcinoma
The MR prostate exam is performed in close cooperation with our registered colleagues, particularly urologists, and can supplement their exams. Examination of the prostate using MRT is a modern diagnostic method in the fight against prostate carcinoma. The method combines various advantages: the organ to be examined can be depicted in different tissue layers. Modern, multiparametric MRI methods using PI-RADS (Prostate Imaging-Reporting and Data System), functional methods can be used along with anatomical MRT methods for decision-making. It is important to find the most aggressive portion of the tumor (index lesion), as this will determine the therapy. In many cases, this requires an MRT of the prostate using PI-RADS. A biopsy planned by our colleagues in urology can be performed more accurately in many cases. The prostate MRI exam using PI-RADS is currently the best option for imaging a prostate carcinoma. This is often, but not always, successful. The Radiology Baden-Baden practice has many years of expertise in the field of MR prostate imaging.
The process does not use any X-ray radiation. Please always clarify in advance whether your insurer will cover at least part of the cost of the examination.
For whom is this exam particularly suitable?
- For men who had a benign finding from a tissue sample (punch biopsy) after elevated PSA was detected, but whose PSA value continues to rise (prostate MRT before second punch biopsy)
- For men who have already had histological confirmation of prostate carcinoma, as an additional decision-making tool for therapeutic decisions (e.g., surgery, radiation, hormone therapy?)
- If the PSA value increases again after surgical removal of the prostate—question: local relapse? Lymph node enlargement in the pelvic region? This sectioned image method is preferred by many radiation institutions for radiation therapy.
MRI mammography
Typical indications
- Post status mastacarcinoma, second carcinoma
Examination of the female breast using MRT can be not only a supplement, but an alternative to X-ray mammography for some women. It can help to clarify certain questions that may have remained open from the mammography and other examination methods for the female breast. The exam should be performed only between days 6-12 after the first day of the period. In the second half of the cycle, the mammary gland tissue changes due to the increased influence of progesterone. This means that the healthy gland tissue also absorbs contrast agent and can no longer be reliably differentiated from diseased tissue.
MRI mammography is used, for example, to precisely examine breast cancer patients before surgery. Post-treatment of patients who have already had breast surgery or breast implants also makes use of MRI mammography. This method supplements conventional X-ray mammography, especially in women with dense tissue structures.
MRI mammography has very high sensitivity for detecting breast tumors that are already growing invasively. Magnetic resonance tomography alone cannot always distinguish benign tumors from malignant ones or from breast cancer precursors (carcinoma in situ). The MRI mammography exam is performed in close cooperation with our registered colleagues, particularly gynecologists, and can supplement their exams.
For whom is this exam suitable?
- For women who have detected changes in breast tissue (such as a palpation finding or abnormalities in X-ray or ultrasound exams). The MRI scan of the breast can also provide information on whether changes to the breast are benign or malignant if the usual early detection exams, such as mammography (X-ray) and ultrasound do not provide reliable evaluation.
- For patients with breast cancer, as an exam prior to surgery in order to rule out additional tumors and plan the surgical procedure. If chemotherapy is needed prior to surgery, its progress and effectiveness can be checked.
- For breast cancer patients in follow-up care, in order to rule out scar relapse (new tumor growth on the scar) with high reliability.
- For women with breast implants (e.g., made of silicone): the implants can interfere with conventional mammography diagnostics (the implant obscures large areas of the gland tissue). The seating and integrity of the implants can also be checked.
- For patients who cannot or do not wish to use X-ray mammography for breast cancer prevention for certain reasons: For example, young women with a family history of frequent breast cancer illness and who require regular early detection screening starting at age 30.
The process does not use any X-ray radiation. Please always clarify in advance whether your insurer will cover at least part of the cost of the examination.
Sellink MRI
Typical Indications
- Chronic inflammatory bowel disease, space-occupying mass in the liver
- Non-specific diarrhea, abdominal pain
The Sellink MRI is performed in close cooperation with our registered colleagues, particularly gastroenterologists, and can supplement their ultrasound and gastrointestinal exams. Magnetic resonance tomography can now be used to produce a comprehensive image of the small intestine. This makes MRT an alternative to conventional small intestine exams according to Sellink (enteroclysis). The Sellink MRI works without a small intestine probe; the contrast agent is simply swallowed.
With MRT, not only changes to the interior of the intestine but also thickening or inflammation of the intestinal wall can the surrounding area can be shown. The examination is particularly well suited for establishing the scope and extent of disease for inflammatory bowel diseases such as Crohn’s disease and colitis ulcerosa.
The process does not use any X-ray radiation.
MRI angiography
Typical Indications
- Cranial vessels
- Throat vessels
- Upper thorax aperture / arms
- Aortic arch and supraaortic branches
- Thoracic aorta
- Abdominal aorta
- Pelvis/legs/feet
MRI angiography allows examination of blood vessels without invasive intervention. We use the MRT to create a three-dimensional model of the vessels. This allows us to determine whether everything is “running smoothly” there. Constrictions and weak tissue (aneurysms) that could cause circulatory dysfunction, stroke, or bleeding can be detected.
The advantage of MRI angiography over conventional X-ray angiography (DSA):
The MRT angiography exam is performed in close cooperation with our registered colleagues, particularly angiologists, and can supplement their ultrasound exams. The standard exam used to be X-ray angiography. A thin tube (catheter) was inserted into the artery from the groin. While X-ray contrast agents were injected through the catheter at high pressure, X-ray images were taken to produce images of the vessel filled with contrast agent.
With MRI angiography, it is no longer necessary to insert a catheter from the groin into the artery. This eliminates the approximately four-hour stay in the outpatient clinic. For MRI angiography, a contrast agent is simply injected into the vein. X-ray radiation is not needed.
Advantages of MRI blood vessel exam
- For MRI angiography, no catheter needs to be inserted into the femoral artery. The contrast agent is simply injected into a vein in the arm.
- The exam can be performed quickly and without the outpatient stay.
- There are no problems with blood clotting or hemorrhaging.
- The contrast agent for MRI angiography does not contain iodine and can also be used in case of hyperactive thyroid.
The process does not use any X-ray radiation.
Full-body MRT
Typical Indications
- Imaging of the entire body
- Tumor diagnostics
- Vascular diagnostics of the entire body
The full-body MRT allows us to image the entire body, that is, all organs, the skeletal system, the spinal column, the vascular system, and the joints. The exam does not replace a dedicated exam of a part of the body, joint, or organ. The exam is primarily used for early detection of cancers. Depending on age and genetic or individual predisposition, other questions such as potential constriction of the arteries can also be clarified. The full-body MRT does not replace gastroscopy or colonoscopy. Please always clarify in advance whether your insurer will cover at least part of the cost of the examination.
The process does not use any X-ray radiation. Please always clarify in advance whether your insurer will cover at least part of the cost of the examination.
Additional MRI exams
- Pancreatic MRI, including MRCP (bile duct imaging)
- Kidney MRI, including urography MRI
- Testicular MRI
- Hydrocolonic MRI
- Cervical/thyroid MRI
- Direct MRI arthrography (joint MRT with contrast agent in the joint)
- Thoracic MRI
- etc.