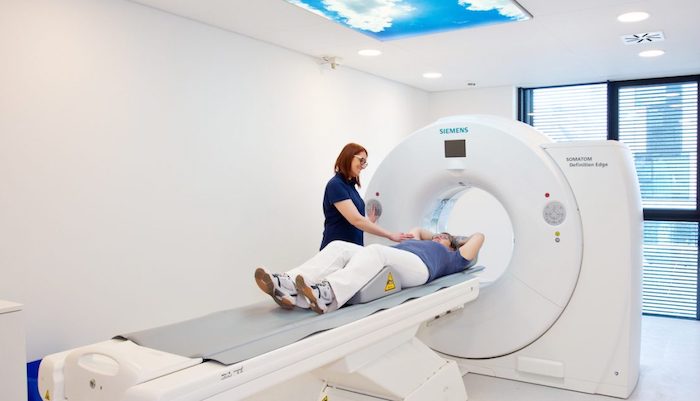
Computed tomography (CT)
Cutting-edge CT technology
In computed tomography (CT), an X-ray tube circles around the patient while simultaneously emitting a thin beam of X-rays. The X-ray radiation used is optimized to an absolute minimum in the Spiral CT system used at Radiology Baden-Baden. With cutting-edge postprocessing tools, the radiation dose has been reduced again to as little as 60% of conventional CT machines. Click here to learn more about our high-end spiral CT …
The exam time for a CT is just a few seconds and because only a ring is used instead of a “tube”, there are no real problems for patients with claustrophobia.
The result is a series of non-overlapping cross section images of the examined body region. The particular advantage over conventional X-rays is improved representation of soft tissues, that is, internal organs. A three-dimensional image can be produced in any plane. Density measurements can also be used to distinguish fatty tissue, fluid, or solid tissue structures.
Important areas of application for computed tomography
Computed tomography has a very broad spectrum of applications today. For lung exams, many abdominal problems, and rapid examination of the head (such as searching for bleeding or injuries), no other method can provide critical information so quickly and precisely. Especially for accidents and strokes, computed tomography is indispensable. Virtual image analysis methods make the body’s internal processes visible to referring colleagues and to the patient.
Even organs that move, such as the beating heart, can now be banished from images. A prerequisite is a very fast and powerful Spiral CT like the one used at Radiology Baden-Baden. Click here to learn more about our high-end spiral CT …
In the field of cardio CT, the Radiology Baden-Baden practice has many years of expertise in close cooperation with surrounding cardiologists and clinics. Cardio CT can be an alternative to heart catheter exams for certain problems. Click here to learn more about cardiac diagnostics at Baden-Baden …
Advantages of computed tomography
Computed tomography is a gentle and, above all, fast examination method with very high detail precision.
Our equipment
The Radiology Baden-Baden practice has what is currently the most modern and lowest radiation SIEMENS-CT in the region, the SIEMENS Edge, with the latest detector and software technology. Using 128-line technology, we can offer our patients an absolute high-end, top-class CT with the SIEMENS Edge. The reduced radiation dose in this CT is as low as 60% relative to conventional CT machines. Click here to learn more about our high-end spiral CT …
Typical application of CT examination
Thorax/abdomen CT
Typical Indications
- Lung imaging, lung vessel imaging (e.g., pulmonary embolism), ruling out tumors
- Abdomen imaging, ruling out tumors, ruling out inflammation
Images of the lungs (thorax) or the abdomen can be used to make a fast, precise declaration.
For an abdominal exam, in order to get an image of the intestine, contrast agent needs to be swallowed starting about 30 minutes prior to the exam.
The process uses a low dose of X-ray radiation and may be performed only by a radiologist.
Cervical CT
Typical Indications
- Ruling out tumors, clarification of swallowing disorder
Images of the neck can be used to make a fast, precise declaration.
The process uses a low dose of X-ray radiation and may be performed only by a radiologist.
Cranial/paranasal sinus CT
Typical Indications
- Ruling out tumors, ruling out internal hemorrhage
- Imaging of the paranasal sinuses (ruling out inflammation)
Images of the skull can be used to make a fast, precise declaration.
No contrast agent is needed for exams of the paranasal sinuses.
The process uses a low dose of X-ray radiation and may be performed only by a radiologist.
Cardiac CT
Typical Indications
- Establishing CHD (coronary heart disease), coronary artery constriction
- Establishing coronary artery calcification
- Checking stents and bypasses
The cardiac CT exam is performed in close cooperation with our registered colleagues, particularly cardiologists, and can supplement their exams. The coronary angiography CT or cardiac CT is performed to rule out constriction of the coronary arteries for a constellation of risks or abnormal complaints. The passability of coronary artery bypass vessels can also be reliably established. The coronary arteries are imaged using CT coronary angiography without a catheter needing to be inserted through the groin.
Things to know about the coronary angiography CT radiation dose
Like the heart catheter exam, X-rays are used for CT coronary angiography, that is, the exam is associated with a dose of radiation. The radiation does varies depending on the problem. The Radiology Baden-Baden practice has the SIEMENS Edge, a 128-line top-class spiral CT that is very fast in order to produce clear, focused images of the beating heart, while remaining very low in radiation. With coronary angiography CT, in many cases a radiation dose of below 1 mSv can be achieved. This dose is significantly lower than the typical dose for a heart catheter—but, of course, if therapy is required then a direct intervention can only be performed via a heart catheter. This means that the radiation load is significantly lower than that which everyone is exposed to from the environment, year after year (approx. 2.5 mSv per year). Click here to learn more about our high-end spiral CT …
Preparation: avoid caffeinated beverages on the day of the examination, and do not take any erectile dysfunction medications (e.g., Viagra) for 24 hours prior to the examination. Click here to learn more about what to look for with cardiac CT …
For whom is this exam suitable?
- For patients with so-called “average or low pre-test probability” of the presence of coronary heart disease (CHD), that is, if the probability of coronary artery constriction requiring treatment is rather low—but it cannot be ruled out entirely. Please speak with us about the question of whether you need CT coronary angiography.
- For patients after aortocoronal bypass operations. In order to evaluate the condition of the bypass vessels, the CT coronary angiography is now an equivalent alternative to a heart catheter exam.
- For patients in whom the passability of a coronary artery must be checked after implantation of stents (blood vessel supports).
Advantages of CT coronary angiography
- Unlike heart catheter exams, no catheter needs to be inserted into the artery.
- The exam is much faster and uses less radiation than a heart catheter exam.
- “White plaque” that has not yet caused constriction of the coronary arteries can only be detected via CT coronary angiography.
The process uses a low dose of X-ray radiation and may be performed only by a radiologist. Please always clarify in advance whether your insurer will cover at least part of the cost of the examination.
CT coronary artery calcification measurement
Typical Indications
- Establishing the calcification of coronary arteries
CT coronary artery calcification measurement is typically performed together with cardio CT. CT coronary artery calcification measurement can be used to establish calcification of the coronary arteries. They are an expression of coronary artery disease, because healthy coronary arteries do not exhibit any calcium. Using computer-aided analysis, we can use standardized criteria to determine whether and to what extent calcification of the coronary arteries exists.
Using comparable values from a large collection of patients, the risk of the presence of coronary heart disease can be estimated as a function of sex and age. If the exam shows large quantities of coronary artery calcification, then coronary heart disease is more likely. Over the long term, the CT coronary artery calcification measurement can also be used to observe the progression of the disease and the success of corresponding therapeutic measures.
For whom is this exam suitable?
For patients who do not have typical complaints, where there are risk factors such as heart attacks in the family history, diabetes, overweight, or smoking, and where a heart catheter exam is not (yet) indicated. No contrast agent is needed.
Things to know about the CT coronary artery calcification measurement radiation dose
X-rays are used for CT coronary artery calcification measurement. The radiation dosage produced is significantly below 0.5 mSv. This means that the radiation exposure is significantly lower than that which everyone is exposed to from the environment, year after year (approx. 2.5 mSv per year).
The process uses a low dose of X-ray radiation and may be performed only by a radiologist. Please always clarify in advance whether your insurer will cover at least part of the cost of the examination.
Sports medicine and musculoskeletal CT diagnostics, Bone density measurement (QCT)
Typical Indications
- High-resolution imaging of joints and bones
- Evaluation of a fracture and fracture healing, including metal implants
- Measurement of bone density (osteodensitometry)
The Radiology Baden-Baden practice is an accredited specialist center for musculoskeletal imaging of the German X-ray Association (Deutschen Röntgengesellschaft). Click here to learn more about certificates held by Radiology Baden-Baden … One focal point of the practice is thus musculoskeletal imaging for diagnosing acute and chronic illnesses and injuries of the entire locomotor system in adults and children. Our practice makes a high-end CT of the latest generation available to patients. In the field of image artifact reduction due to implants, for example after breaking a bone, the use of a special post-processing tool such as iMAR (iterative metal artifact reduction) can make possible a significant improvement in image quality and thus in the diagnosis for this latest generation of equipment.
Of course, we also offer bone density measurement (QCT) for early detection or monitoring the progression and therapy of osteoporosis. Click here to learn more about our high-end spiral CT …
The process uses a low dose of X-ray radiation and may be performed only by a radiologist.
Low-dose pulmonary CT
Typical Indications
- Ruling out tumors in the lungs
- Pulmonary inflammation
- Pulmonary embolism
The low-dose pulmonary CT exam is performed in close cooperation with our registered colleagues, particularly pneumologists, and can supplement their exams. Lung cancer in particular can be diagnosed very gently and reliably using so-called low-dose computed tomography. When true details are needed, however, such as before therapy, a “normal” CT of the lungs is typically still needed, because the image resolution is then more detailed than for a low-dose CT. Using the extremely low-dose, top-class CT available to our patients, however, the radiation load is still very low, even in this case. Click here to learn more about our high-end spiral CT …
Using cutting-edge technology, tumors just a few millimeters in diameter can be discovered.
The procedure is therefore very suitable as an early detection measure for patients with increased risk of lung cancer (e.g., heavy smokers). In addition to its application as an early detection method for lung cancer, we also use low-dose pulmonary CT to clarify diseases that relate solely to the lungs (e.g., asbestosis, sarcoidosis) and for tumor searches in high-risk patients.
Advantages and disadvantages of early lung cancer detection using computed tomography
- Low-dose CT using multilayer technology is currently the most sensitive method for early lung cancer detection.
- Low-dose CT increases the chance of recovery, as lung cancer tumors can be detected at very early stages.
- With low-dose pulmonary DT, lung cancer tumors that are “hidden” behind vessels and crests in the diaphragm can also be detected. The conventional methods do not register such tumors.
- Using the computer-aided analysis that we perform as a standard on the CT data, the volume of a tumor can be measured precisely and the slightest change in size can be detected. A CT progression exam every three to six months can be used to differentiate benign tissue changes from malignant ones without a doubt, due to the lack of change in size.
- The introduction of new detector systems allow lung exams to be performed on modern CT equipment with a very low radiation dose. Using multilayer CT technology with the SIEMENS Edge, the radiation exposure is just a fraction of the original CT exams.
The process uses a low dose of X-ray radiation and may be performed only by a radiologist.
Dental-CT
Typical Indications
- Diagnostics of changes to the tooth and tooth root
- Planning implants and dental surgery interventions
In many cases, dental surgery interventions require imaging that is as precise and low in radiation as possible. Using appropriate image-processing methods and 3D visualizations, potential interventions can be planned as well as possible in advance. This makes for the best possible results for the patient. Our practice makes a high-end CT of the latest generation available to patients. In the field of image artifact reduction due to implants, the use of a special post-processing tool such as iMAR (iterative metal artifact reduction) can make possible a significant improvement in image quality and thus in the diagnosis for this latest generation of equipment. Contrast agent is needed only in exceptional cases.
Virtual colonoscopy
Typical Indications
- Non-invasive imaging of the large intestine
- Detecting polyps and tumors in the colon
The virtual colonoscopy, also known as CT colonography, is performed in close cooperation with our registered colleagues, particularly gastroenterologists, and can be a supplement to their exams. Tumors and colon polyps as small as 6 mm can be detected early using this procedure.
For special cases, the virtual colonoscopy can be a supplement to the gastroscopy or colonoscopy (gastrointestinal exam) performed by the gastroenterologist. Examples include impassibility of a segment of the colon for the endoscope, or explicit refusal of an endoscope. The virtual colonoscopy does not eliminate the need for purgative measures.
For a virtual colonoscopy, no endoscope needs to be inserted into the interior of the colon. The “trip” through the large intestine is instead “simulated” on the computer monitor. Any polyps cannot be removed and further analyzed, unlike conventional colonoscopy.
Based on previous findings, the method has similar reliability to conventional colonoscopy for finding colon polyps or colon cancer in sizes of above 6 millimeters.
Preparation: purgative measures similar to colonoscopy.
Advantages and disadvantages of virtual colonoscopy
- For a virtual colonoscopy, no endoscope needs to be inserted into the interior of the colon.
- The CT colonoscopy does not cause any pain or require any sedative.
- The physician cannot remove any tissue samples (biopsies) during the exam. If changes in the colon are suspected, therefore, a normal colonoscopy must always be performed in addition.
The process uses a low dose of X-ray radiation and may be performed only by a radiologist. Please always clarify in advance whether your insurer will cover at least part of the cost of the examination.
Additional CT exams
- Hydrogastric CT
- Hydro-pancreas CT
- Full-body low-dose CT
- Abdominal/pelvic CT
- Hydro-pancreas CT
- Hydrogastric CT